Why Fluid Lubrication is Critical for Padded Reaming
Correct set-up of the padded reamer is critical to successful reaming, but proper selection of a metalworking fluid is also crucial for sufficient lubrication and emulsion properties that efficiently carry fines, help minimize defects, maximize throughput and increase tool life.
Posted: January 10, 2018
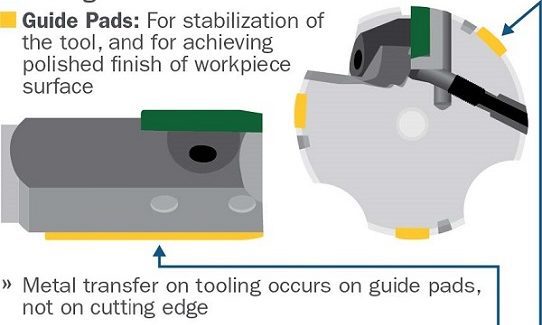
Padded reamers are utilized throughout manufacturing to generate the final hole geometry and meet demanding surface finish tolerances. Some examples of padded reamer applications are automatic transmission valve channels, engine valve guides and engine crankbore/ cambores. Since the reaming process is one of the last manufacturing steps prior to assembly, it is extremely important to optimize the process to reduce costly scrap. As the name implies, the padded reamer differs from a fluted reamer in that the padded reamer has a cutting surface and guide pads that ride on the diameter of the hole to put pressure on the cutting surface, which generates the hole size and geometry. The guide pads also act as a burnishing tool to help provide a smooth surface finish.
Since the pad forces are “riding” on the inside surface of the hole, significant lubrication is necessary in padded reamer operations to eliminate scratches on the hole surface and maintain the required surface finish. Lubrication is especially critical for the first guide pad after the cutting surface. This means metalworking fluids play a very critical role in the optimization of padded reamer applications for the following reasons:
- Metal adhesion to the reamer pads is one of the primary routes to failure and loss of surface finish. Inadequate lubrication of the padded reamer may result in scratches in the bore from aluminum pick-up on the guide pads leading to surface finish issues. The primary purpose of the metalworking fluid is to supply a sufficiently thick film to maintain low friction between the workpiece and the guide pad surfaces. This film prevents metal adhesion and subsequent surface finish degradation.
- Fines from the cutting operation have been shown to be a significant mechanism of failure in the padded reaming operation. Chips and fines need to be efficiently carried to the filtration system for removal from the machining process. Significant fines build-up will be carried into the guide pad/metal interface and negatively impact the surface finish.
- Optimal metalworking fluids for padded reamers need to provide lubrication of the guide pads but also carry the fines from the point of cut. These properties are inversely related in the fact that more lubrication means an “oilier” emulsion and this typically carries more fines. A “tighter” emulsion typically carries fines more effectively but lacks the lubrication necessary at the pad/metal interface.
- Inadequate cooling at the point of cut can result in non-conforming hole geometry and premature reamer wear.
- Many reamer applications utilize through-the-tool coolant systems that require a metalworking fluid to operate at higher pressures without foaming. Excessive foaming will adversely affect the coolant pumps and reduce the coolant delivery to the point of cut.
Although proper set-up of the padded reamer is one of the most critical steps in the success of the reaming process, the proper selection of a metalworking fluid is crucial. Padded reaming requires a metalworking fluid that offers the necessary lubrication properties to give sufficient film thickness and emulsion properties to that will efficiently carry fines, help minimize defects, maximize throughput, and increase tool life. For example, QUAKERCOOL® 7450 is a high performance semi-synthetic fluid technology that is designed for critical reaming applications and provides excellent tapping performance in heavy-duty machining operations, such as on automotive and aerospace aluminum alloys. This fluid delivers significant improvements in reaming applications at product concentrations lower than typical soluble oil technology, and offers the following operational benefits:
- Its unique formulation provides the necessary lubrication at the pad/metal interface for critical surface finish requirements while also maintaining extremely efficient fines handling for enhanced padded reamer performance.
- It contains excellent foam and emulsion stability properties for high pressure through-the-tool coolant reamer applications.
- It insures proper metalworking fluid delivery to the point of cut.
- It can be run at water hardness ranges from 0 ppm to 500 ppm and is very stable with increasing magnesium hardness from machining aluminum castings.
- Its enhanced biostability package resists bacteria and fungus, extends sump life, and has minimal plant odors.
- Its formaldehyde and boron free technology improves residue and meets HSE compliance.